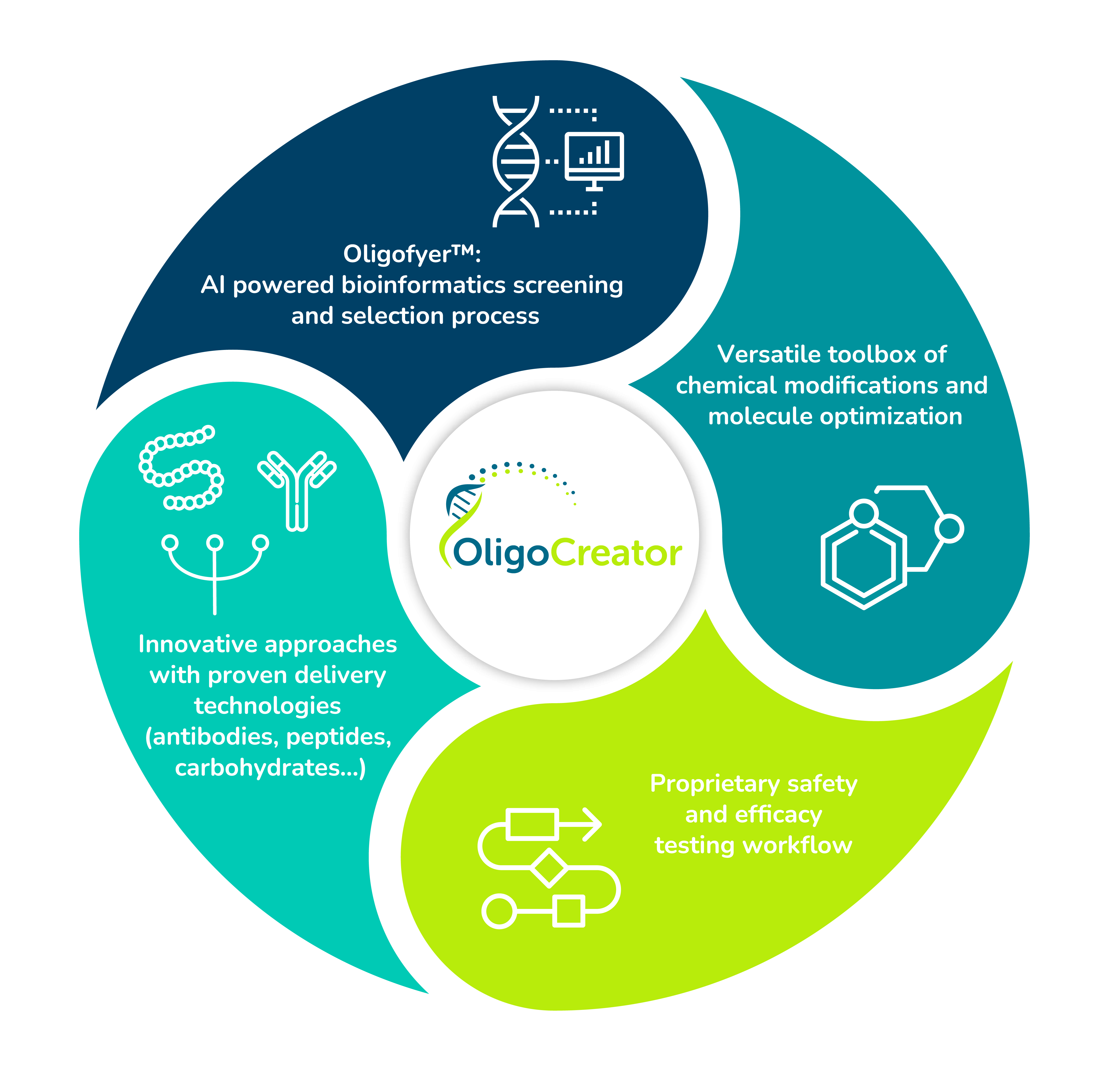
OligoCreator®
Our AI-empowered oligonucleotide discovery and development platform, combines both innovative and proven delivery modalities with the precision and specificity of oligonucleotides.
We have established deep expertise as well as a network of collaboration partners that allows us to combine our knowledge and expertise in the field of oligonucleotides with the specialized knowledge of our partners in their respective delivery modalities. This enables us to accurately target specific organs or tissues, transforming untreatable conditions into treatable ones.
Our OligoCreator® platform features our proprietary safety and efficacy testing systems, ensuring every therapeutic candidate undergoes thorough scrutiny and rigorous evaluation in the discovery phase, thereby mitigating safety risks early on and allowing a broad therapeutic window of our drug candidates.
Our platform includes a comprehensive toolbox of chemical oligonucleotide modifications that enable fine-tuning of oligonucleotide properties such as reduction of immune-stimulatory potential or off-target toxicities.
With OligoCreator®, we've greatly expedited the drug discovery process, from target selection to development, identifying and characterizing safe and efficacious therapeutic candidates at unparalleled speed. Compared to small molecules or complex biologics, our rational design and rapid discovery process greatly reduces costs and time spent.
Our unique AI-powered bioinformatics selection process is constantly enhanced with wet lab data to refine our prediction algorithms. To date, data from over 50 projects have been leveraged to optimize our in-silico selection strategy, resulting in an exceptionally high hit rate in our in vitro and in vivo safety and efficacy screens.
Combining innovative and proven delivery
modalities with the precision and specificity of oligonucleotides
OligoCreator® has been validated by numerous collaborations with pharma, biotech and academia as well as our proprietary projects. Our R&D efforts regularly lead to publications and presentations at high-ranking scientific journals and conferences, highlighting the quality of our research and technology team and leadership.
Oligonucleotides:
A highly precise therapeutic approach
Oligonucleotides are short sequences of DNA or RNA, that, among others, can be created to bind to specific RNA sequences. Depending on their design, they can – for example – induce degradation of the target RNA, thereby preventing target protein expression, or modulate RNA splicing, thereby changing protein sequence and function. Antisense oligonucleotides (“ASOs”), a certain class of oligonucleotides, can be designed to inhibit the function of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) or microRNAs (miRNAs), which is an evolving field of novel targets across multiple indications. Oligonucleotides are incredibly versatile molecules that can be customized to specifically target and modify aberrant RNA transcripts, offering potentially beneficial therapeutic approaches in the handling of difficult-to-treat disorders. With their innate characteristics and unique mechanism of action, antisense oligonucleotides or siRNA have several advantages over a number of current therapeutic approaches:
Drugging the undruggable: All targets encoded by RNA as well as non-coding RNAs can effectively and specifically be addressed
Rapid drug development: From target identification to clinic in less than two years feasible
Rational design: Availability of whole-genome sequence data allows elimination of unspecific sequences during the in silico sequence selection process
Versatile and adaptable: Toolbox of different chemistries enables rapid molecule optimization and conjugation to targeting modalities
Holistic targeting approach: Simultaneous suppression of all functions of a target protein by downregulation of target expression
Publications and references
Our research & development efforts have led to numerous publications and presentations in high-ranking scientific journals and conferences:
October 2024; Nucleic Acid Therapeutics; Characterization of the TLR9-Activating Potential of LNA-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides; Characterization of the TLR9-Activating Potential of LNA-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides - PubMed
October 2024; The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology; Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-specific antisense oligonucleotides reduce infection with SARS-CoV-2 variants; Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-specific antisense oligonucleotides reduce infection with SARS-CoV-2 variants - PubMed
May 2024, Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer; Dual TLR9 and PD-L1 targeting unleashes dendritic cells to induce durable antitumor immunity; Dual TLR9 and PD-L1 targeting unleashes dendritic cells to induce durable antitumor immunity - PubMed
July 2023, The Journal of Immunology; Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy Decreases IL-1β Expression and Prolongs Survival in Mutant Nlrp3 Mice; Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy Decreases IL-1β Expression and Prolongs Survival in Mutant Nlrp3 Mice - PubMed
June 2023, eLife; Identification of Paired-related Homeobox Protein 1 as a key mesenchymal transcription factor in pulmonary fibrosis; Identification of Paired-related Homeobox Protein 1 as a key mesenchymal transcription factor in pulmonary fibrosis - PubMed
July 2022; Journal of Lipid Research; ANGPTL4 silencing via antisense oligonucleotides reduces plasma triglycerides and glucose in mice without causing lymphadenopathy; ANGPTL4 silencing via antisense oligonucleotides reduces plasma triglycerides and glucose in mice without causing lymphadenopathy - PubMed
December 2021; Journal of the American Society of Nephrology; CHOP-ASO Ameliorates Glomerular and Tubular Damage on Top of ACE Inhibition in Diabetic Kidney Disease; CHOP-ASO Ameliorates Glomerular and Tubular Damage on Top of ACE Inhibition in Diabetic Kidney Disease - PubMed
December 2021; Nucleic Acid Therapeutics; Investigation of the Activity of Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Multiple Genes by RNA-Sequencing; Investigation of the Activity of Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Multiple Genes by RNA-Sequencing - PubMed
February 2021; Cancer Research; Therapeutic Targeting of Metadherin Suppresses Colorectal and Lung Cancer Progression and Metastasis; Therapeutic Targeting of Metadherin Suppresses Colorectal and Lung Cancer Progression and Metastasis - PubMed
January 2021; Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy; Using RNA-seq to Assess Off-Target Effects of Antisense Oligonucleotides in Human Cell Lines; Using RNA-seq to Assess Off-Target Effects of Antisense Oligonucleotides in Human Cell Lines - PubMed
September 2020; Molecular Therapy. Nucleic Acids; Preventing ATP Degradation by ASO-Mediated Knockdown of CD39 and CD73 Results in A2aR-Independent Rescue of T Cell Proliferation; Preventing ATP Degradation by ASO-Mediated Knockdown of CD39 and CD73 Results in A2aR-Independent Rescue of T Cell Proliferation - PubMed
January 2020; Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy; A highly efficient modality to block the degradation of tryptophan for cancer immunotherapy: locked nucleic acid-modified antisense oligonucleotides to inhibit human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1/tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase expression; A highly efficient modality to block the degradation of tryptophan for cancer immunotherapy: locked nucleic acid-modified antisense oligonucleotides to inhibit human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1/tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase expression - PubMed
June 2019; Molecular Therapy. Nucleic Acids; Anti-Niemann Pick C1 Single-Stranded Oligonucleotides with Locked Nucleic Acids Potently Reduce Ebola Virus Infection In Vitro; Anti-Niemann Pick C1 Single-Stranded Oligonucleotides with Locked Nucleic Acids Potently Reduce Ebola Virus Infection In Vitro - PubMed
March 2019; Nature Communications; ER stress-induced mediator C/EBP homologous protein thwarts effector T cell activity in tumors through T-bet repression; ER stress-induced mediator C/EBP homologous protein thwarts effector T cell activity in tumors through T-bet repression - PubMed
March 2019; Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer; Antisense oligonucleotide targeting CD39 improves anti-tumor T cell immunity; Antisense oligonucleotide targeting CD39 improves anti-tumor T cell immunity - PubMed